SGUL LOB's for CVS: Acute Coronary Syndrome/ Myocardial Infarction (MI).
Pinned to
62
0
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Andrew Street
over 8 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Andrew Street
over 8 years ago
|
|

982 S & Sx of acute MI.
983 The common mechanism to all ACS (STEMI, NSTEMI, unstable angina) is r..... or erosion of the fibrous c..... of a coronary artery p..... This leads to platelet aggregation and adhesion, localized t....., vasoconstriction and distal thrombus embolization. Thrombus formation and the v..... produced by platelet release of serotonin and thromboxane A2, results in myocardial i..... due to reduction of coronary b..... f.....
984 Describe the emergency Ix that should be performed to confirm the Dx of MI.
985 Give criteria for Dx of MI.
986 What are two key questions in determining Rx/Mx of ACS?
986 Describe the immediate Mx of a pt with STEMI.
986 Describe the immediate Mx of a pt with NSTEMI.
992 Unstable angina refers to angina of recent onset (<..... h) or a deterioration in previous s..... a..... with Sx frequently occurring at ....., i.e. acute coronary syndrome
992 What is the difference between unstable angina & NSTEMI?
993 Describe S & Sx of unstable angina.
994 List Ix that should be performed in a pt with unstable angina.
995 Immediate Mx of unstable angina.
995 Ongoing Rx for a pt with confirmed unstable angina.
997 List indications for urgent cardiological intervention.
998 Describe which vessels supply which myocardiaal regions.
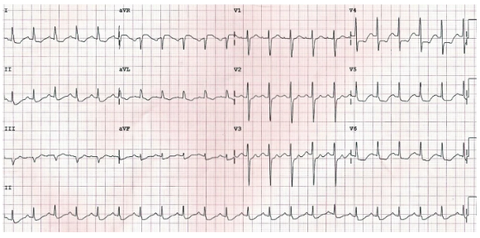
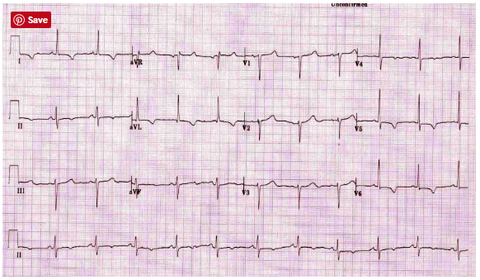
999 Explain how an ECG can be used to determine the site of MI & indicate which vessel is occluded.
1000 Describe the evolution of ECG changes following an MI.
1002 List complications of MI.
1007 List drugs proven to improve prognosis following MI and give evidence supporting their use.

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards