A Levels Psychology Flashcards on AS: Approaches - Biopsychology, created by Julia Romanów on 19/03/2016.
Pinned to
193
18
0
No tags specified

|
Created by Julia Romanów
over 8 years ago
|
|
Close

|
Created by Julia Romanów
over 8 years ago
|
|

What is a neuron?
There are 3 types of neurons...
Sensory neuron functions?
Motor neuron functions?
Relay neurons
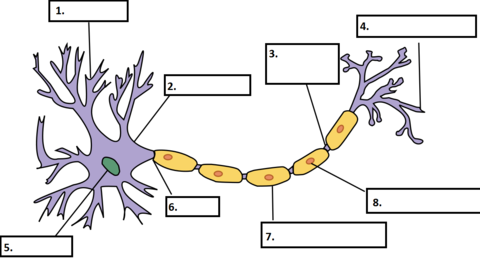
Axon: A long extension from the cell body which nerve impulses are sent through.
Myelin sheath: fatty material that surrounds, insulates and protects the axon.
Synaptic cleft: a gap between axon terminals and dendrites.
Signals cross this gap in the form of neurotransmitters.
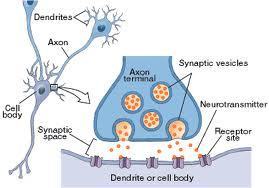
Briefly describe synaptic transmission
The nervous system has many divisions...
the sympathetic and parasympathetic Ns's work in opposition...
physiological changes due to sympathetic NS state....
physiological aspects of parasympathetic ns state...
Made up of glands that secretes chemicals called hormones into the blood stream.
Examples:
Pituitary gland
Thyroid
Adrenals
Testes
Ovaries
Briefly describe the process of 'fight or flight mode'...
Strengths of this approach
Weaknesses of this approach
What are twin studies?
Monozygotic twins (identical)
100% shared genes
same sex
develop from one egg/embryo that splits
Twin studies are evaluated based on their concordance rates (%)
If Mz twins have a genetically hereditary trait that only one seems to have it could be caused by the environmental factors.
why?
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
this condition illustrates the importance of environmental factors (on the phenotype)

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards