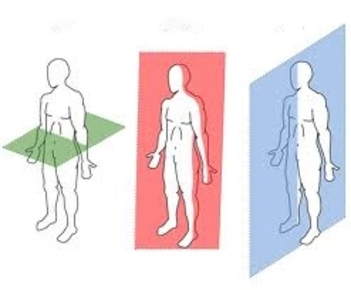
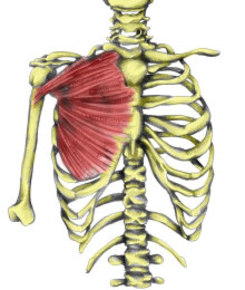
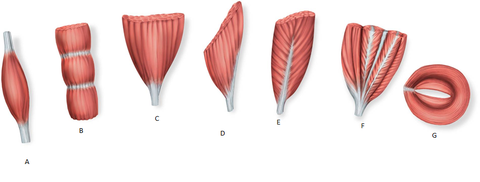
Flashcards on Anatomical terms, Skin, Muscles, Blood Vessels, Bones, created by Joanna Elliott on 10/11/2013.
Pinned to
134
3
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Joanna Elliott
about 11 years ago
|
|
Close