Revision for Open University S294 Module.
Pinned to
326
2
0
No tags specified

|
Created by Glen Rooney
over 3 years ago
|
|
Close

|
Created by Glen Rooney
over 3 years ago
|
|

What are the energy sources and carbon sources of chemoautotrophs?
What are myosins?
What does ubiquitin do?
What are microtubules made of?
Define growth factors
Name the 3 main types of cell surface receptors and give an example of a ligand involved in their interaction.
Define aneuploidy
What are the 4 key features of cell communication?
What are the energy sources and carbon sources of photoautotrophs?
Why would protons cross the inner mitochondrial membrane via an uncoupler rather than via ATP synthase?
What are dyneins?
What is an allosteric effector?
What are the proteins that attach the extracellular matrix to the cell membrane?
Name the 3 muscle cell types and their function
What is Rho-family GTPase?
What do chaperones do?
What are mitogens?
How do retinoblastoma act as a break in the cell cycle?
What is an example and function of an adipocyte?
What is the main component of its cytoplasm?
What is meant by amphipathic?
What is the microtubule organising centre (MTOC)?
Phosphorylation is catalysed by the enzyme ___________.
Dephosphorylation is catalysed by the enzyme __________.
If an energetically unfavourable reaction is coupled to an energetically favourable, the change in free energy (∆G) of the overall process must be _________ for it to occur.
What is chemotaxis and chemotropism?
What is RME?
What are the 3 major roles of general transcription factors?
Polypeptides are synthesised in which direction?
What is the energy source and carbon source of photoheterotrophs?
Can ions be moved against their concentration gradient?
What is the difference between competitive and non-competitive inhibitors?
What organelle packages and tags proteins for proper distribution in the cell?
What is feedback inhibition?
Define what is meant by a metabolic pathway.
What are integrins?
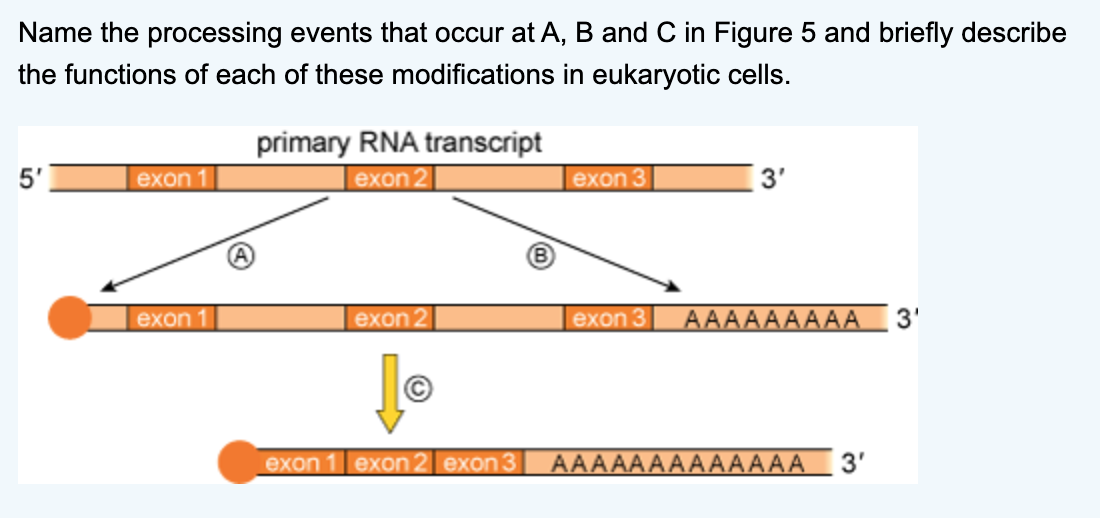
What happens to the 5' and 3' ends of mature mRNA during post-transcriptional modification?
What do proteasomes do?
What is the energy source and carbon source of chemoheterotrophs?
Synthesis of the RNA transcript occurs in which direction?
What are the 2 forms of cell division carried out by complex eukaryotes?
What is a motor protein?
Are potassium levels higher inside or outside an animal cell?
And is the membrane potential of a non-excited cell positive, negative or neutral?
What are sense strands and antisense strands?
What is the function of red blood cells?
Name 2 features of red blood cells.
The sum of catabolism and anabolism is __________.
MCPs that bind a repellant are ________ while those that bind an attractant are __________.
What are kinesins?
Give examples of support cells (connective tissue cells).
What is their function?
What is a fibroblast?
Define transcription factors
RNA polymerase reads the base sequence of the template strand in which direction?
What are the stages (in order) of meiosis?
What are the 2 main ways in which an enzyme can be controlled in metabolism?
Name some examples of coenzymes and describe their function and key features .
What is an endergonic reaction?
What is the difference between a nucleolus and a nucleoid?
What are MCPs and what domains do they have?
What are the stages of mitosis in order?
What are the cells of the immune system?
Where would you find epithelial cells and what is their function?
Examples, function and features of nerve cells (neurons).
Examples, function and features of endocrine cells.
What is endocytosis and exocytosis?
What biomolecules are required for in vitro DNA synthesis in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
What are oligonucleotides?
Why does DNA synthesis require oligonucleotides to act as primers in PCR?
What are the 3 phases of each round of PCR and what temperatures do they occur?
What DNA polymerase is commonly used in PCR?
What are restriction endonucleases?
What processes in living cells require DNA ligase?
What is the link reaction and where does it take place?
What are the names of these cell cycle checkpoints and what is monitored at each one?
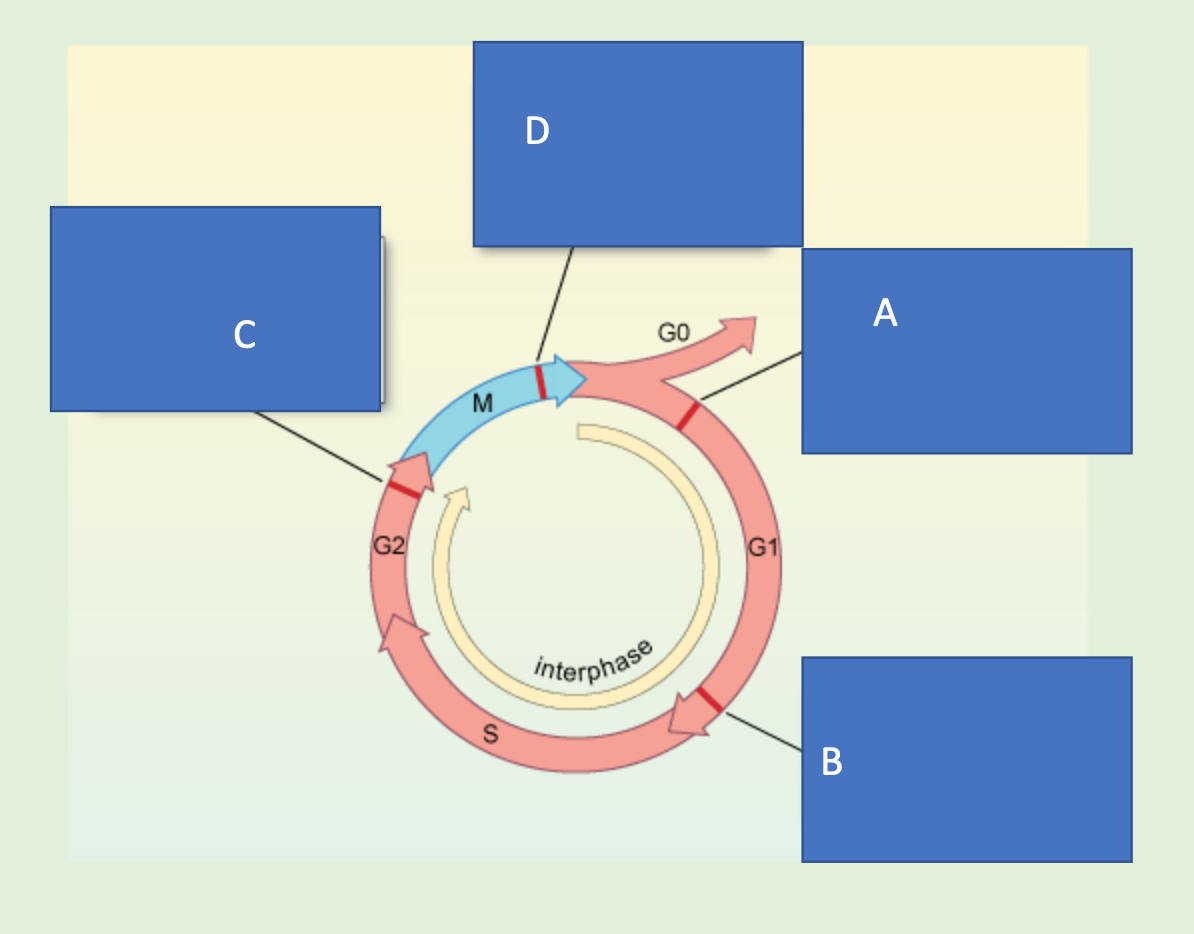
What is the role of p53 in the cell cycle?
What is peptidoglycan?
Give three examples of the shapes exhibited by different bacterial species, and name one species of bacterium that exhibits each shape.
Name the three main types of tissue in flowering plants and state the functions of each of these types of tissue.
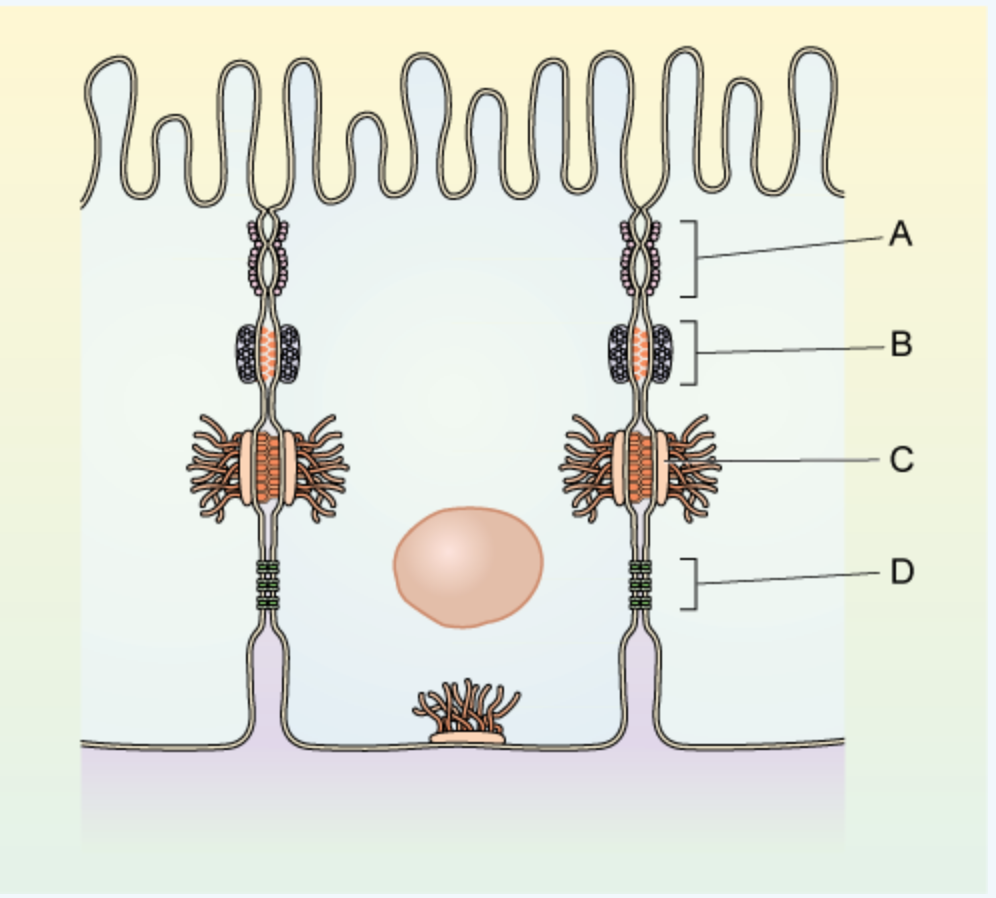
Name the structures labelled A, B, C and D and state their functions.
What is a nonsense mutation?
What is a null mutation?
What happens in a transition mutation?
What happens in a transversion mutation?
What is a frameshift mutation?
What are the different types of non-coding DNA found in the human genome?
In eukaryotes there are two main groups of transcription factors. What are they? Give a specific example of each type.
Some proteins are synthesised as inactive precursors known as ________.
What is the lipid raft hypothesis?
What is the Tm of a cell membrane?
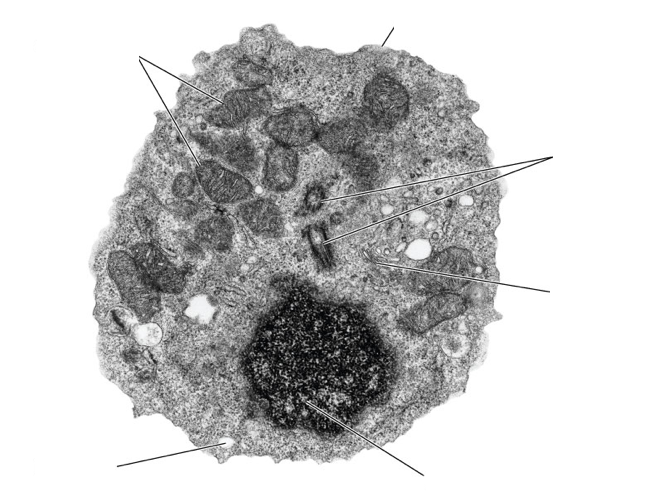
List at least five features of microtubules
How is motor protein activity rendered essentially irreversible?
What are transposons?
What are the three types of protein filament that make up the cytoskeleton?
What are their component proteins and what are their main functions?
What are telomeres?
What is the difference between immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards