Entire Organics Paper revision flashcards
Pinned to
251
6
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Millie Aitken
about 11 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Millie Aitken
about 11 years ago
|
|

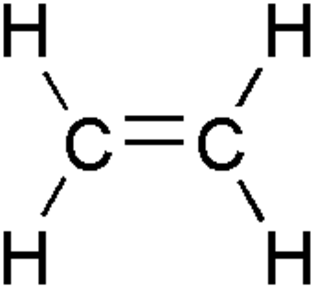
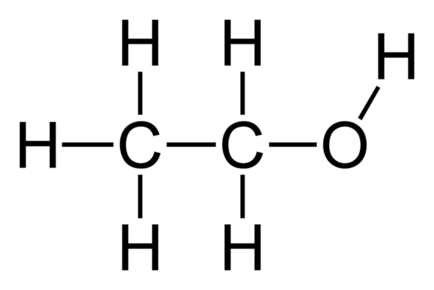
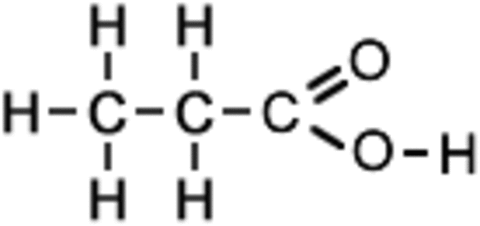
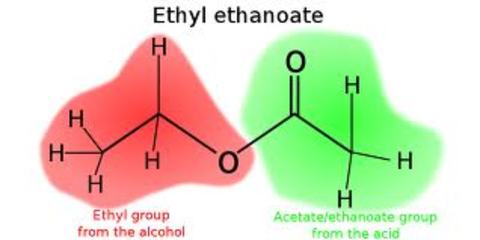

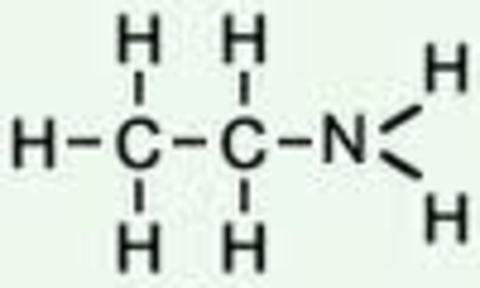
Alkenes:
+ MnO4- -->
+ H2O/H2SO4 -->
+ H2 Ni Catalyst -->
+ HBr -->
+ Br2
Haloalkanes:
+ Alcoholic KOH
Alkanes:
+ steam cracking
+ Br2 U.V. light
Haloalkanes:
+ Alcoholic NH3
Amines:
+ di-amine
+ di-acid
+ acyl chloride
Alcohols:
+ Conc. H2SO4
+ diols/carboxyllic acids and condensation
Secondary Alcohol:
+ H+/Cr2O72- and heat
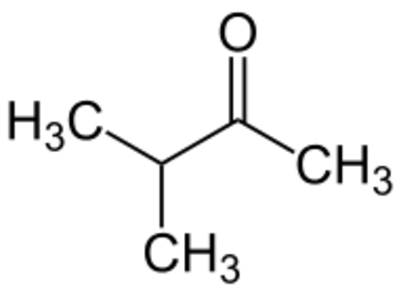
Ketones:
+ Na BH4 + OH-
Sugars:
Undergo fermentation to form...
Primary Alcohols:
+ H+/Cr2O72- and Heat
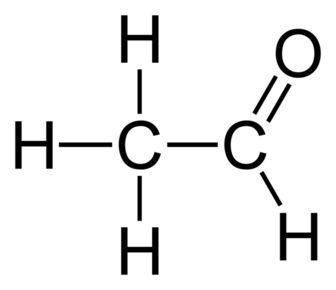
Aldehydes:
+ Na BH4
+ H+/Cr2O72- and Heat reflux
Carboxylic acids:
+ Metals/carbonates/bases
+ Alcoholic H2SO4
+SOCl2 or PCl3
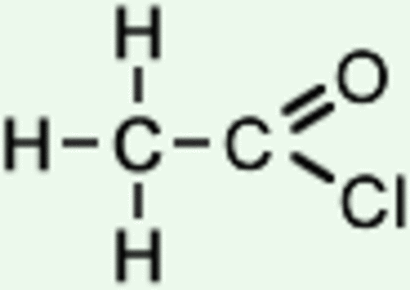
Acyl Chlorides:
+ H20 (vigorous reaction)
+ Alcohol
+ Alcoholic NH3
+ Amine
Geometrical isomers occur in _____ and are different in terms of ______. They form ____ and ____ isomers.
Structural isomers:
They are the rearrangement of ___________________________________________________________________.
Optical isomers (enantiomers):
The molecule needs a ________________ and it reflects _____________________________________________________________.
Markovnikov's rule:
What is it?
What type of reactions does it work for?
What type of compounds does it not occur for?
Electrophile
Nucleophile
Saytzeff's rule:
Alkanes:
Preparation
Combustion
Substitution
Melting/boiling points
Alkenes:
Combustion
Preparation
Melting/Boiling points
Alkynes:
Combustion
Preparation
(Acetylene = ehtyne)
Alcohols:
Classification and how each class reacts
Alcohols:
Melting/boiling points
Alcohols:
Isomerism - what type of isomers can sometimes occur?
Why?
Alcohols:
Preparation
Alcohols:
Combustion
Why can't you smell Ethanol gas?
Primary Alcohols undergo ___________ reactions with just about any _____________________.
Ethanol -(H+/MnO4-)->
What has happened if a reaction of ethanol with permanganate does not produce a carboxylic acid?
Secondary alcohol reaction:
Propan-2-ol -(H+/MnO4-)->
Tertiary alcohols only oxidise if you ______________________ however the molecule falls apart => cannot be oxidised.
Markovnikov and Saytzeff's rules produce _______ products ___% of the time and _________ products __% of the time.
Saytzeff's rule can only occur from the ___________ products of Markovnikov's rule.
Acyl Chlorides:
Preparation
What type of reactions do acyl chlorides undergo compared to carboxylic acids?
Acyl chlorides:
Reactions -with water
- with ammonia
- with amines
- with alcohols
Esters:
- Why are they not formed via elimination?
- Preparation
Carboxylic acid and alcohol react in equilibrium to form ___________ when ____________ is used as a catalyst and a reflux is used?
What type of smell foes an ester have and what is it commonly used in?
How are polymers formed?
Hydrogen Bonding:
It is the strength of _______ and ___________________ interactions between molecules.
Hydrogen Bonding:
Some compounds have ______________ forces that are much stronger than ordinary ______________ forces.
How do you identify an alkene?
How do you identify an alkyne?
How do you identify an alcohol?
How do you identify an aldehyde?
How do you identify an amine?
How do you identify a carboxylic acid?

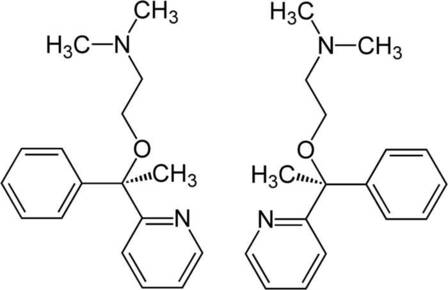
Nucleophilic Substitution

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards