Flashcards on OCR AS Biology, created by joshbrown3397 on 15/01/2015.
Pinned to
1242
90
0
|
|
Created by joshbrown3397
almost 10 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by joshbrown3397
almost 10 years ago
|
|

This organelle functions in cellular respiration
The organelle functions to package and deliver protiens
Cell organelles are located within the (__________) of the cell
The Endoplasmic reticulum functions to
Genetic material is contained within the (___________) of the cell
This organelle is responsible for destroying worn-out cell parts
The (__________) controls what enters and leaves the cell
The rough endoplasmic reticulum has (__________) located on it
Located within the nucleus, it is responsible for producing ribosomes
Which structure is directly responsible for the formation of proteins within a cell?
What part of the cell is responsible for the breaking down and digesting of things
Identify the organelle pictured
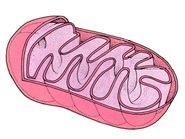
What part of the cell serves as an intracellular highway?
Which of the following would you NOT find in a bacterial cell?
A)DNA
B)Cell Membrane
C)Golgi apperatus
D)Ribosomes
Which of the following is found in plant cells but not animal cells?
A)Cell wall
B)Vacuole
C)Mitochondria
D)Endoplasmic reticulum
The jellylike interior of the cell is called the
Identify the organelle
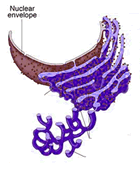
What part of the cell makes protiens
Where are the ribosomes usually located in animal or plant cells?
What part of the cell serves to process, package and export protiens?
What is cell signalling?
The function of a glycolipid is
What do channel proteins allow?
What do phospholipids do?
What does cholesterol do in the membrane?
Glycoproteins are...
How does a protein enter the cell
How does a sodium ion enter the cell?
How does water enter a cell?
How does oxygen enter the cell?
How does alcohol enter the cell?
The molecule that a signal molecule binds to is _________
The membrane contains binding sites which are
The signal molecule has a shape that is
The shape of the binding site and the shape of the signal molecule are
Cell signalling occurs when signal molecules bind to molecules on the
An example of a cell signalling molecule is
Modern drugs often act by mimicking the action of
How does heating affect cell membranes?
What happens in anaphase?
What happens is metaphase?
Prophase
What happens in Telophase?
The elastic fibres function is to
The function of blood is to
The function of cartilage during inhilation is to
The function of a goblet cell is
The function of smooth muscle is to
The function of squamous epithelium is to
The function of ciliated epithelium is to
Single-celled organisms have a _______ surface area to volume ratio
In large animals the surface area to volume ratio is
Active organisms need a lot of
Do single-celled organisms need a 'pump'?
Large organisms have a large surface area but a very large...
True or false: Ventilation helps to increase the concentration of oxygen in the aveoli
True or false: A low concentration of oxygen in the blood facilitates diffusion
True or false: Carbon dioxide leaves the blood by osmosis
True or false: The alveoli have ciliated epithelium
True or false: Elastic fibres contract to reduce the size of the alveoli
True or false: Elastic fibres help to expel air from the alveoli
True or false: During inhilation, the intercostal muscles contract
True or false: The alveoli contain smooth muscle fibres
True or false: The alveoli are stretched as more air enters the lungs
True or false: A short diffusion pathway helps to create a steep concentration gradient
True or false: A short diffusion pathway helps to maintain a steep concentration gradient
True or false: Cartilage keeps the airways rigid
True or false: Tidal volume must be measured at rest

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards