The structure and function of skin, including the effects of the environment on the skin
Pinned to
164
4
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Hannah Tribe
about 10 years ago
|
|
Close
|
|
Created by Hannah Tribe
about 10 years ago
|
|

Give 4 main functions of skin
How is the skin involved in metabolism?
How is the skin involved in thermoregulation?
How is the skin involved in sensation?
What is the skin a barrier from?
What are the 2 basic layers of skin?
What are the 4 layers of the epidermis, from superficial to deep?
What other layer could there be? Where might it be found in the body and between which layers is it?
What are the characteristics of the stratum corneum? (3)
What are the characteristics of the stratum granulosum?
What are the characteristics of the stratum spinosum? (2)
What are the characteristics of the stratum basale? (3)
What are desmosomes?
What are Langerhans cells?
What are Merkel cells?
What are the 2 types of melanin?
What is directly underneath the stratum basale?
What are the arrows pointing to and what are they?
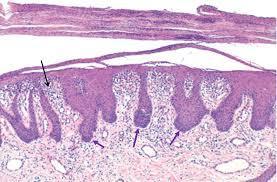
How do friction blisters form?
What is vitiligo?
What are the 2 basic layers of the dermis?
What can be found in the dermis? (6)
What is found in the upper papillary dermis?
What is found in the deep reticular dermis?
How is blood flow to the skin controlled?
What are the 2 main types of nerve supply to the skin?
What different types of sensory fibres could be found in the dermis? (5)
What is below the dermis and what can be found there?
What is the function of it? (3)
Where does hair growth begin?
What are the characteristics of the hair bulb? (2)
Why are hair and nails hard, yet skin is soft?
What surrounds hair follicles and what is its function?
What glands are associated with hair follicles?
What is their function?
Name 2 types of sweat gland present in the skin.
What general structure do sweat glands have?
Where are apocrine glands found?
Where are Eccrine sweat glands found?
What are the differences between apocrine and eccrine sweat glands? (4)
What are 2 simple functions of vitamin D?
What does vitamin D deficiency lead to?
Give 3 reasons why death might occur following extreme epidermal damage?
Give 5 environmental insults to the skin
How does the skin adapt itself to friction?
How does the skin adapt itself to protect against UV radiation?
What are the features of melanocytes? (2)
What is the destination of the melanosomes and what is their purpose?
How does UV damage cause extra protecting against UV radiation?
How is this adaptation visible?
What is the term for extreme hyperkeratosis? What is the cause of it?
What are the levels of UV radiation emitted from the sun and what is the difference between them?
What is sunburn and what are the risks of it?
Why do people tend to get wrinkles when they are exposed to the sun for prolonged periods of time?
What is the scientific name for moles?
How are moles formed?
What is the scientific name for freckles?
How do people get freckles? Are there any risks?
What are 'age spots'?
What is another risk of UV radiation on the skin?
What are the 2 main types of skin cancers and which cells do they involve?
What are the 2 sub-types of non-melanoma?
Why are melanomas so dangerous?
What is UV radiation on the skin useful for?
What are the 2 main types of contact dermatitis?
How does allergic contact dermatitis arise?
What is the scientific name for a fungal/bacterial nail infection?
Give 2 examples of bacterial skin infections
Give an example of a viral skin infection
How can infections enter the skin? Who is more likely to get skin infections?
What is the cause of atopic eczema?
What occurs in the acute stage of atopic eczema?
What occurs in the chronic stage of atopic eczema?
Where is commonly affected by atopic eczema?
Why does itching cause more of an itch?
What treatments can be given for eczema?
What can be caused if eczema is co-infected with herpes virus?
What is psoriasis?
How does psoriasis differ from eczema?
What are the treatments for psoriasis? (7)
What causes acne vulgaris?
What are the 2 aims of treatment of acne vulgaris?
What is impetigo?
What causes viral warts?
What is tinea?
How is it treated?
What is actinic keratosis?
What can be the prognosis of actinic keratosis?
What is the other type of carcinoma that can develop in the skin?
How is it treated?
What is the ABCDE of suspicious pigmented lesions?
What is the consequence of finding suspicious pigmented lesions?
What is Breslow thickness?
How is it significant?

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards